I’ve recorded an impression – a sort of review – for There Is No Anti-Memetics Division by QNTM.
I’ll allow the content to speak for itself. tl;dr? I like it.
Author

I’ve recorded an impression – a sort of review – for There Is No Anti-Memetics Division by QNTM.
I’ll allow the content to speak for itself. tl;dr? I like it.

Working with an editor shouldn’t be scary. Unless, of course, you frighten easily.
Let’s begin with the great paranoia of writers everywhere: They’ll steal my idea! Relax. No one’s skulking through the shadows waiting to pinch your half-finished manuscript about a misunderstood vampire who paints feelings. Ideas are cheap. They rain down like confetti. The reason every other book or film feels vaguely familiar isn’t because everyone’s plagiarising everyone else; it’s because there are only so many ways to dress the same skeleton. Your story’s clothing — the style, the voice, the rhythm — that’s what matters.
And honestly, ask yourself if your idea is really so revolutionary. Probably not. I sometimes test mine on an AI just to see if the collective hive mind has already beaten me to it. Usually it has. I just tilt it differently. Star Wars? A Western in space. Lucas literally invited Joseph Campbell over to discuss myth templates, then sprinkled some lasers on top. Nothing wrong with that — unless you start believing it’s unique.
Now, what does an editor actually do? They read your work and offer feedback. When that happens, you’ve basically got three choices:
I. Ignore it. Maybe the suggestion feels wrong. Good. Trust that feeling. Nothing’s worse than bowing to authority and regretting it later. Imagine the post-publication chorus: Why on earth did you do that? — and your only defence is, Well, my editor said so. Pathetic. Give twelve editors the same chapter, you’ll get twelve different answers. Writing has rules, yes — but most are decorative.
II. Accept it. Hit ‘Accept all revisions’. Voilà — you’re suddenly brilliant. It’s tidy, efficient, and possibly catastrophic.
III. Consider it. The middle ground. Let the note spark something else entirely. Maybe they’re wrong about what to fix but right that something’s off.
Some advice will be structural, some grammatical. Both are optional. I, for one, commit grammatical heresy whenever my characters open their mouths. People don’t speak like Oxford dons; they stumble, repeat, and misuse words spectacularly. Editors sometimes flag this as ‘awkward’. I call it ‘human’. Grammar is for dissertations. Dialogue is for life.

I don’t read sci-fi. It rarely resonates with me. I’ve read many classics, but I don’t get the hype. As a speculative fiction author, I sometimes operate in an adjacent space – close enough to borrow a few ideas, but never quite belonging. I’m not interested in fetishising technology or celebrating so-called human ingenuity. But if an idea serves the story? I’ll use it.
One concept I wanted to explore: the definition of life itself, and what sentience means when we can barely define it for ourselves.
Not long ago, I began working on a story: some people leave Earth to inhabit another planet in a different solar system. Nothing revolutionary there. They land on what appears to be an uninhabited world – uninhabited, that is, by our current definition of life. Instead, the planet itself is alive. Not in the Gaia hypothesis sense of interconnected ecosystems, but truly interactive. Responsive. Alien in ways that challenge every assumption about consciousness.
Of course, there are more details – dual suns in a figure-eight orbit, shifting gravity, time that expands and contracts, organisms that defy classification. But those are mechanics. The heart of the story is simpler: what happens when survival requires abandoning the frameworks that made you human?
As is my protocol, I fed my manuscript into AI and asked: is this idea unique? If not, what’s it similar to? Who am I adjacent to?
I got names. Titles. Books and films. Most had superficial similarities but different intents. Then one stood out: Solaris, Stanisław Lem’s 1961 novel. I hadn’t read it, so I got a copy.
There were so many commonalities it felt like discovery and defeat in equal measure.
Lem wrote Solaris before humans had meaningfully left Earth’s atmosphere. Published in 1961, it predated material space exploration by years. On October 4, 1957, the Soviets launched Sputnik 1 – the first artificial satellite. Four years later, Yuri Gagarin became the first human to orbit Earth, his flight lasting just 108 minutes. The first American in space, Alan Shepard, flew in 1961. John Glenn orbited in 1962.
Lem imagined a sentient ocean on an alien world orbiting twin suns before we’d even confirmed planets existed beyond our solar system. His protagonist grapples with a consciousness so alien that communication may be impossible – not because of language barriers, but because shared reference points don’t exist.
In some ways, Solaris also shares DNA with Jeff VanderMeer’s Annihilation – that same sense of an environment that isn’t hostile so much as indifferent, operating by rules humans can barely perceive, let alone comprehend. But where VanderMeer leans into existential dread, Lem’s tone is colder, more philosophical. Less visceral horror, more intellectual vertigo.
My story, working title: Goldilocks, sits somewhere between them. It has Lem’s alien sentience and dual-sun orbital mechanics. It has VanderMeer’s gradual unravelling of human perception and sanity. But it also has something neither quite touches: the brutal intimacy of being the last of your species, seeking warmth in a universe that offers none.
So is my idea original? Not entirely. Does that matter? I’m not sure anymore.
Lem wrote his novel sixty years ago, before we’d touched the moon, before we knew what exoplanets looked like, before we’d meaningfully begun asking whether consciousness requires a brain. He imagined sentience beyond human comprehension – and did it so thoroughly that anyone following feels like they’re retracing his steps.
But perhaps that’s the point. Originality isn’t about being first. It’s about what you do with inherited ideas – how you refract them through your own obsessions, anxieties, and questions.
Lem asked: can we ever truly know an alien intelligence?
VanderMeer asked: what happens when the environment rewrites you?
I’m asking: what does it mean to be human when humanity itself is ending?
Maybe that’s enough distance. Maybe it’s not. Either way, the story exists now – half-written, haunted by its predecessors, searching for its own voice in the silence between stars.

I don’t want to develop a reputation as an AI apologist – I really don’t. But I do want to strip away the veneer humans so lovingly lacquer over themselves: the idea that art is some mystical emanation of a “soul,” accessible only to those blessed by the Muse and willing to suffer nobly in a garret.
Rachel Barr argues that AI art can never be the same as human art, no matter how “perfect,” because AI has no feelings or drive. Cue the violins. These arguments always seem to hinge on metaphysical window-dressing. When Rachel says “we”, she’s not talking about humanity at large; she’s talking about herself and a very particular subset of humans who identify as artists. And when she invokes “masters”, the circle shrinks still further, to the cloistered guild who’ve anointed themselves the keepers of aesthetic legitimacy.
But here’s the bit they’d rather you didn’t notice: feelings and drive aren’t prerequisites for art. They’re just one of the many myths humans tell about art, usually the most flattering one. Strip away the Romantic varnish and art is often craft, habit, accident, repetition. A compulsive tic in oil paint. A mistake on the guitar that somehow worked. A poet bashing words together until something sticks.
And I say this not as a detached observer but as a writer, artist, and musician in my own right. I sympathise with the instinct to defend one’s turf, but I don’t need to steep myself in hubris to retain self-worth. My work stands or falls on its own. It doesn’t require a metaphysical monopoly.
So when someone insists AI art can never be “the same,” what they mean is it doesn’t flatter our myths. Because if an algorithm can spit out a perfect sonnet or an exquisite image without the tortured soul attached, then what have we been worshipping all this time? The art itself, or the halo around the artist?
Perhaps the real fear isn’t that AI art lacks feelings. It’s that human art doesn’t require them either. And that’s a blow to the species ego – an ego already so fragile it cracks if you so much as ask whether the Mona Lisa is just paint on a board.

As per my recent post, I need a sanity break. I’ve been editing Needle’s Edge all day. Each time I hit a milestone, I consider drafting a blog post, but then I choose to persist. Not this time.
I’ve been untangling the spaghetti of a misplaced – or rather, overextended – pregnancy. It had stretched on for too long, so I weeded out contradictory events. Some of these had dependencies, so I relocated or eliminated them to preserve flow.
In the process, I re-oriented her conception date and reset any foreshadowing that tied into it. To keep myself honest, I started tracking her progress in the manuscript with markers: <p=X>. With each time-specific event, I increment X.
So far, I’ve reviewed 24 sequential scenes, not counting the half-dozen relocated ones I had to rework just enough to maintain continuity. This leaves the protagonist at 29 weeks. That also meant pruning irrelevant references, for instance, cutting any mention of pregnancy before it even began.
Being a typical human pregnancy, my target is 38 to 40 weeks. That leaves me with another 10-odd weeks to rummage through. Once I’ve untangled the draft, I still need to return for line edits, colour, and shape.
Editing is often pitched as polishing, but sometimes it’s surgery. Today, I’ve been elbows-deep in the operating theatre.

This is as much a reminder for me as a PSA. Time is the most limited resource you’ve got.
Consider your goals, and plan accordingly. Not everyone has concrete goals. As writers, we likely do. Finish that sentence, that page, that chapter, that draft, those edits, that book…
There’s social media – that’s this place – video games, partying, family and mates, eating and sleeping. Whatevs.
And don’t forget to take care of your mental health.
You may have many goals – or just one or two. Consider opportunity costs.
This blog post is distracting me from my editing. Still, I want to share. maybe it will help you.
Perspective is key.
Define your goals. Prioritise them. Make it happen.
Go away now!

Editing Needle’s Edge has taken longer than the time it took to draft the damned thing. Typical, I suppose, but demoralising all the same. Drafting is a rush; editing is a grind. In video game parlance, this is the endless dungeon crawl. Kill the same mob again and again, collect marginal XP, and hope that –eventually – you level up.
Recently, I wrestled with the narrative structure, which was starting to feel like Inception with a side order of Russian dolls. Flashbacks within flashbacks within flashbacks. I diagrammed it, mostly to convince myself I hadn’t lost the plot (see exhibit A, below).
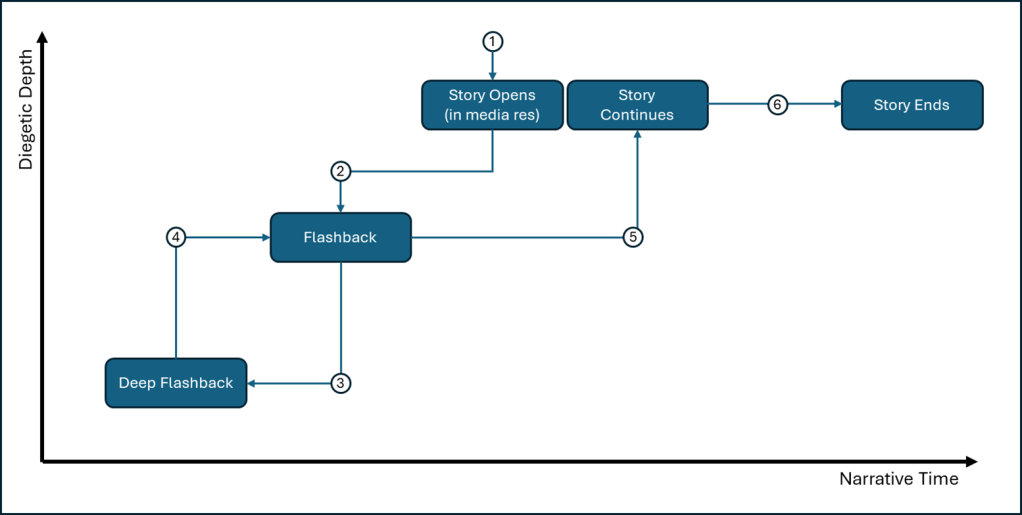
Here’s the lay of the land—without spoilers, of course. The story begins [1] in medias res, with Sarah-slash-Stacey already entrenched in her daily grind. Then comes [2] the flashback, showing how she arrived there. Midway through, we plunge into [3] a deep flashback of her childhood, before [4] snapping back to the mid-flashback, then finally [5] rejoining the present-day storyline until [6] the bitter – or possibly bittersweet – end.
Naturally, I subvert as many tropes as I can, though no one can write a tropeless story any more than they can write one without words. (I’m sure some post-structuralist is trying right now, but God help their readers.)
The hardest part wasn’t constructing the labyrinth but finding my way out again – reengaging with the present-day thread after chapters of detour without resorting to that televisual clanger: “We now return to our regularly scheduled programming.”
Editing a book like this is less polishing and more archeology: chiselling away sediment, brushing off centuries of dust, desperately hoping not to snap the artefact in half. With luck, the grind pays off. If not, at least I’ll have a lovely flowchart to show for it.

Congratulations, you’ve finished a manuscript. You’ve pushed the boulder uphill, typed “The End,” and maybe even convinced yourself you’re done. Spoiler: you’re not. This is where beta readers come in — those kind souls who’ll slog through your draft and tell you whether it sings, stumbles, or just sits there like porridge. The trouble is, most writers don’t actually know what to ask them, and so they end up with feedback about as useful as a horoscope.
The first and most uncomfortable question is about intent. What are my goals in writing this, and did you see them? Most writers never ask, because it forces them to say what they meant in the first place. Are you interrogating free will? Trying to write a page-turner? Smuggling philosophy under the hood of a dystopian thriller? If your beta doesn’t see it, either you buried it too deep or you didn’t put it in at all. Of course, not every writer works with some grand meta in mind, but if you do, this is the question that makes or breaks the project.
If your story feels like homework, you’ve already lost.
Enjoyment comes next, even if it bruises the ego. Did they actually like reading it? If your story feels like homework, you’ve already lost. It’s better to know this from a sympathetic reader now than from Goodreads later. A related angle is pacing: where did the story drag? Readers know exactly where they reached for their phone, even if they’re too polite to say so without prompting. Ask them to point to the spots where the air went out of the room.
Did the conclusion feel like it belonged to the story’s own logic?
Characters are another litmus test. Which ones did they care about, and which ones left them cold? Writers are often too close to notice when a protagonist reads like cardboard, or when a side character steals the oxygen. Beta readers are your lab rats here, revealing who’s magnetic and who’s forgettable. The same goes for endings. Don’t ask if it was happy – ask if it was satisfying. Did the conclusion feel like it belonged to the story’s own logic? If the reader feels cheated, the manuscript isn’t finished.
World-building deserves its own interrogation, especially in speculative fiction. Readers will happily forgive dragons, AI dictators, or interstellar chalk drawings, but not inconsistency. If the rules of your world shift without reason, they’ll notice. In fact, coherence is more important than cleverness. The reader doesn’t need to understand every mechanism, but they do need to trust that you do.
Was there an image, a phrase, a scene that stayed with them once the book was closed?
Finally, ask what lingered afterwards. Was there an image, a phrase, a scene that stayed with them once the book was closed? That’s your gold. Double down on it. If nothing sticks, you’ve got polishing to do.
One last but often overlooked question is about the reader themselves: am I asking the right person? An excellent sci-fi enthusiast might not be your best pick for YA urban fiction. A romance aficionado won’t necessarily grasp the rhythms of a philosophy-laden dystopia. Fit matters. You wouldn’t ask a vegan to taste-test your steakhouse menu, so don’t ask the wrong reader to bless your book.
Am I asking the right person?
And here’s the tightrope for the beta reader: they are not there to tell you the book they would have written. Their job is to respond to the book you actually put on the page. It’s your manuscript, not a co-authorship audition. If their feedback starts with “what I would have done,” that’s not critique – that’s a rewrite.
The meta point is simple. Beta readers are not editors. They aren’t there to fix your commas or restructure your second act. Their value is in telling you what it feels like to read your book – hot, cold, flat, or electric. And if you’ve got a grand philosophical undercurrent humming beneath the surface, they’re the only ones who can tell you whether it came across.
Beta readers are not editors.
So don’t hand your beta readers a scalpel and ask them to perform surgery. Hand them your story and ask: did you taste what I meant to cook?

Zach Cregger wrote Weapons. He also directed it, produced it, and composed the soundtrack. This blog is about writing, so let’s stay with that. In a recent interview with Perri Nemiroff at Fandango, he described how the story emerged almost by accident:
Perri asks Zach how he got the idea for the story:
I didn’t have an idea for the movie when I started writing
— Zach Cregger
I was like, “Okay, little girl telling a story— takes place at a school. Kids go to school. Follow a teacher. Class is empty. Why? I don’t know. Let’s find out.”
And then two sentences later – because the kids all ran out the night before.
Okay, that’s a hook I like. So, I knew… I have a good question. So then, I probably wrote 50 pages before I even knew what the answer was going to be, honestly.
So, you know, I got the teacher, I got the angry dad, and they’re kind of doing their cat and mouse sort of a thing, and then… I got this cop, and… it wasn’t until about the midpoint where I had… what it was.
And that was a really good moment for me because I was like, “This might not ever be a thing. I might not have anything here.”
You know, if I don’t have a good answer, there’s no reason to watch this movie.
That’s pantsing in its purest form — starting with a question and running fifty pages before you even know if there’s an answer. Discovery writing at its most precarious: equal parts exhilaration and existential dread.
Personally, I lean hybrid. Sometimes I pants a draft until it coughs up a structure; other times I start with scaffolding and let the innards misbehave. But the dead ends always loom. I’ve euthanised countless ideas that failed to evolve, rather than stitching them together with some lazy deus ex contrivance. (Television thrives on that sort of duct-taped plotting, which is precisely why I don’t bother with it.)
Anyway, I have not seen this movie. I am not a fan of horror, but every now and then I sample what’s out there. I might check this out to see how well it delivers.

Critics never tire of reminding us that AI has no emotions, as though this were some startling revelation. Next, perhaps, they’ll inform us that penguins can’t fly and that bankers are allergic to honesty. Yes, generative AI has no emotions. But must we wheel in the fainting couches? Writers don’t need it to sob into its silicon sleeve.
Full disclosure: I am a writer who writes fiction and non-fiction alike. I am also a language philosopher; I study language. And a technologist. I’ve been working with artificial intelligence since the early ’90s with Wave 3 – expert systems. I am still involved with our current incarnation, Wave 4 – generative AI. I know that artificial intelligence has no intelligence. I also know that intelligence is ill-defined and contains metaphysical claims, so there’s that…
Meantime, let’s stroll, briskly, through three ghosts of philosophy: Saussure, Wittgenstein, and Derrida.
Ferdinand de Saussure gave us the tidy structuralist package: the signified (the thing itself, say, a tree) and the signifier (the sound, the squiggle, the utterance “tree,” “arbre,” “árbol”). Lovely when we’re talking about branches and bark. Less useful when we stray into abstractions—justice, freedom, love—the slippery things that dissolve under scrutiny.
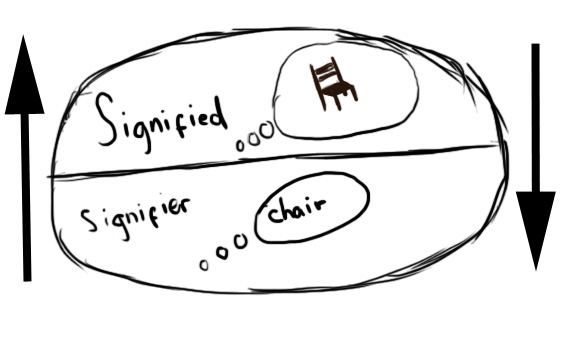
Still, Saussure’s model gets us so far. AI has consumed entire forests of texts and images. It “knows” trees in the sense that it can output something you and I would recognise as one. Does it see trees when it dreams? Do Androids Dream of Electric Sheep? Of course not. But neither do you when you define one.
René Magritte‘s famous painting reminds us that the reference is not the object.

Ludwig Wittgenstein, that glorious thorn, tore the Saussurean comfort blanket to shreds. Words, he said, are not tethered to the world with neat strings. They define themselves by what they are not. A tree is a tree because it is not a cow, a kettle, or an Aston Martin.

Take a dictionary entry:
tree
/trē/
noun
a woody perennial plant, typically having a single stem or trunk growing to a considerable height and bearing lateral branches at some distance from the ground.
What’s woody? What’s perennial? If you already speak English, you nod along. If you’re an alien with no prior knowledge, you’ve learned nothing. Dictionaries are tautological loops; words point only to more words. If you want to play along in another language, here’s a Russian equivalent.
дерево
/derevo/
существительное
древесное многолетнее растение, обычно имеющее один стебель или ствол, растущий до значительной высоты и несущее боковые ветви на некотором расстоянии от земли.
AI, like Wittgenstein’s alien, sits inside the loop. It never “sees” a tree but recognises the patterns of description. And this is enough. Give it your prompt, and it dutifully produces something we humans identify as a tree. Not your tree, not my tree, but plausibly treelike. Which is, incidentally, all any of us ever manage with language.
Enter Jacques Derrida with his deconstructive wrecking ball. Language, he reminds us, privileges pairs—male/female, black/white—where one term lords it over the other. These pairs carry emotional weight: power, hierarchy, exclusion. The charge isn’t in the bark of the word, but in the cultural forest around it.
AI doesn’t “feel” the weight of male over female, but it registers that Tolstoy, Austen, Baldwin, Beauvoir, or Butler did. And it can reproduce the linguistic trace of that imbalance. Which is precisely what writers do: not transmit private emotion, but arrange words that conjure emotion in readers.
I recently stumbled on the claim that AI cannot “read.” Merriam-Webster defines reading as “to receive or take in the sense of (letters, symbols, etc.), especially by sight or touch.” AI most certainly does this—just not with eyeballs. To deny it the label is to engage in etymological protectionism, a petty nationalism of words.
Here is the uncomfortable truth: when you write, your own emotions are irrelevant. You may weep over the keyboard like a tragic Byronic hero, but the reader may shrug. Or worse, laugh. Writing is not a syringe injecting your feelings into another’s bloodstream. It is a conjuring act with language.
AI can conjure. It has read Tolstoy, Ishiguro, Morrison, Murakami. It knows how words relate, exclude, and resonate. If it reproduces emotional cadence, that is all that matters. The question is not whether it feels but whether you, the reader, do.
So yes, AI has no emotions. Neither does your dictionary. And yet both will continue to outlast your heartbreak.